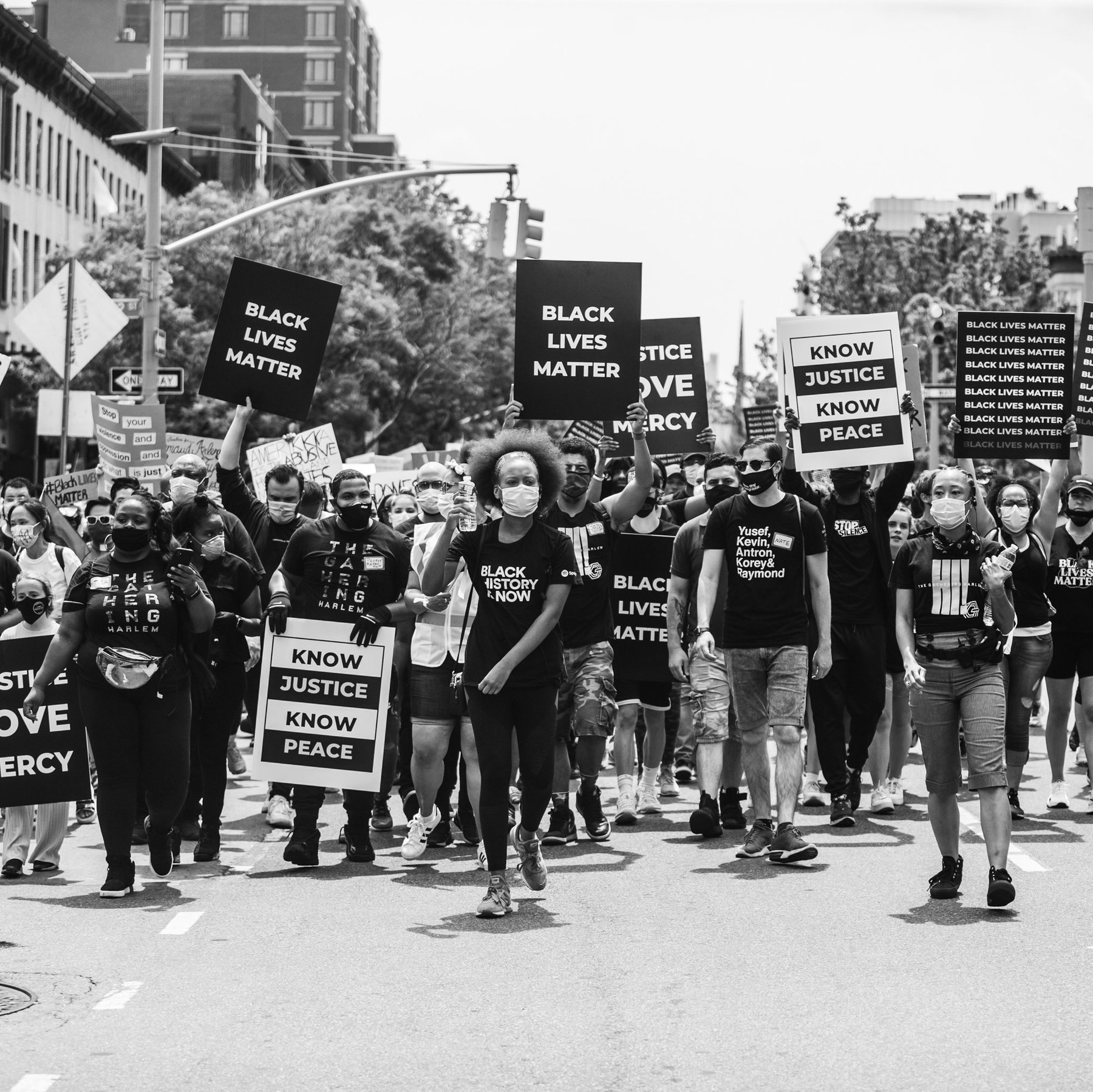
If true justice and equality are ever to be achieved in the United States, the country must finally take seriously what it owes black Americans.
– By Nikole Hannah-Jones
It feels different this time.
Black Americans protesting the violation of their rights are a defining tradition of this country. In the last century, there have been hundreds of uprisings in black communities in response to white violence. Some have produced substantive change. After the assassination of the Rev. Dr. Martin Luther King Jr. in 1968, uprisings in more than 100 cities broke the final congressional deadlock over whether it should be illegal to deny people housing simply because they descended from people who had been enslaved. The Fair Housing Act, which prohibits housing discrimination on the basis of race, gender and religion, among other categories, seemed destined to die in Congress as white Southerners were joined by many of their Northern counterparts who knew housing segregation was central to how Jim Crow was accomplished in the North. But just seven days after King’s death, President Lyndon B. Johnson signed the act into law from the smoldering capital, which was still under protection from the National Guard.
Most of the time these uprisings have produced hand-wringing and consternation but few necessary structural changes. After black uprisings swept the nation in the mid-1960s, Johnson created the Kerner Commission to examine their causes, and the report it issued in 1968 recommended a national effort to dismantle segregation and structural racism across American institutions. It was shelved by the president, like so many similar reports, and instead white Americans voted in a “law and order” president, Richard Nixon. The following decades brought increased police militarization, law-enforcement spending and mass incarceration of black Americans.
The changes we’re seeing today in some ways seem shockingly swift, and in other ways rage-inducingly slow. After years of black-led activism, protest and organizing, the weeks of protests since George Floyd’s killing have moved lawmakers to ban chokeholds by police officers, consider stripping law enforcement of the qualified immunity that has made it almost impossible to hold responsible officers who kill, and discuss moving significant parts of ballooning police budgets into funding for social services. Black Lives Matter, the group founded in 2013 by three black women, Patrisse Khan-Cullors, Alicia Garza and Opal Tometi, after the acquittal of Trayvon Martin’s killer, saw its support among American voters rise almost as much in the two weeks after Floyd’s killing than in the last two years. According to polling by Civiqs, more than 50 percent of registered voters now say they support the movement.
The cascading effect of these protests has been something to behold. The commissioner of the N.F.L., which blackballed Colin Kaepernick for daring to respectfully protest police brutality, announced that the N.F.L. had, in fact, been wrong and that black lives actually do matter. (Kaepernick, on the other hand, still has no job.) HBO Max announced that it would temporarily pull from its roster the Lost Cause propaganda film “Gone With the Wind” — which in classically American fashion holds the spot as the highest-grossing feature film of all time. NASCAR came to the sudden realization that its decades-long permissiveness toward fans’ waving the battle flag of a traitorous would-be nation that fought to preserve the right to traffic black people was, in fact, contrary to its “commitment to providing a welcoming and inclusive environment for all fans, our competitors and our industry.” Bubba Wallace, the only full-time black driver at the sport’s top level, who had called on NASCAR to make the move, drove victory laps in an all-black stock car emblazoned with the words “#BLACKLIVESMATTER.”
Multiracial groups of Americans have defaced or snatched down monuments to enslavers and bigots from Virginia to Philadelphia to Minneapolis and New Mexico, leading local and state politicians to locate the moral courage to realize that they indeed did have the power to purge from public spaces icons to white supremacy. Even the University of Alabama, the place where Gov. George Wallace quite literally stood in the schoolhouse door to try to block the court-ordered admission of two black students, a place whose Grecian-columned campus and still largely segregated sororities pose the living embodiment of Dixie, is removing three plaques honoring Confederate soldiers and will study whether to rename buildings holding the monikers of enslavers and white supremacists after a student-led campaign garnered more than 17,000 signatures.
Unlike so many times in the past, in which black people mostly marched and protested alone to demand recognition of their full humanity and citizenship, a multiracial and multigenerational protest army has taken to the streets over the last month. They’ve spread across all 50 states in places big and small, including historically all-white towns like Vidor, Texas, where as recently as 1993 a federal judge had to order its public housing integrated. Shortly after, white supremacists ran out of town the handful of black people who had moved in. That Vidor, Texas, which remains 91 percent white and 0.5 percent black, held a Black Lives Matter rally in early June. In countries as disparate as England, Brazil, Kenya and Turkey, crowds pumped fists and carried signs with George Floyd’s name.
And this month, a Monmouth University poll showed that 76 percent of Americans, and 71 percent of white Americans, believe that racial and ethnic discrimination is a “big problem” in the United States. Just a few years ago, little more than half of white Americans believed that. The numbers in the Monmouth poll were so high that it left some political scientists questioning the poll’s quality.