By Sabrina Strings
About five years ago, I was invited to sit in on a meeting about health in the African-American community. Several important figures in the fields of public health and economics were present. A freshly minted Ph.D., I felt strangely like an interloper. I was also the only black person in the room.
One of the facilitators introduced me to the other participants and said something to the effect of “Sabrina, what do you think? Why are black people sick?”
It was a question asked in earnest. Some of the experts had devoted their entire careers to addressing questions surrounding racial health inequities. Years of research, and in some instances failed interventions, had left them baffled. Why are black people so sick?
My colleagues looked befuddled as they tried to come to terms with my reply.
I meant what I said: The era of slavery was when white Americans determined that black Americans needed only the bare necessities, not enough to keep them optimally safe and healthy. It set in motion black people’s diminished access to healthy foods, safe working conditions, medical treatment and a host of other social inequities that negatively impact health.
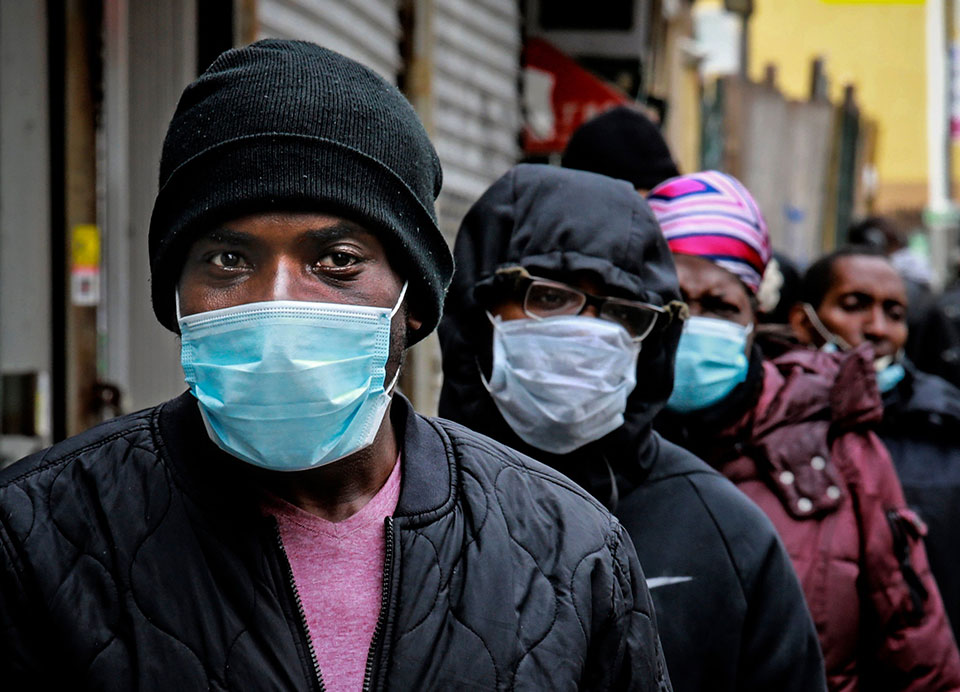
This message is particularly important in a moment when African-Americans have experienced the highest rates of severe complications and death from the coronavirus and “obesity” has surfaced as an explanation. The cultural narrative that black people’s weight is a harbinger of disease and death has long served as a dangerous distraction from the real sources of inequality, and it’s happening again.
Reliable data are hard to come by, but available analyses show that on average, the rate of black fatalities is 2.4 times that of whites with Covid-19. In states including Michigan, Kansas and Wisconsin and in Washington, D.C., that ratio jumps to five to seven black people dying of Covid-19 complications for every one white death.
Despite the lack of clarity surrounding these findings, one interpretation of these disparities that has gained traction is the idea that black people are unduly obese (currently defined as a body mass index greater than 30) which is seen as a driver of other chronic illnesses and is believed to put black people at high risk for serious complications from Covid-19.
Read full article →